Points¶
There are two data structures to represent a point in two-dimensional space, of coordiantes \((x, y)\):
![digraph Point2D {
Point2D -> "CPoint2D*"
"CPoint2D*" -> x
"CPoint2D*" -> y
"CPoint2D*" [fillcolor=gray,style="rounded,filled"]
x [fillcolor=gray,style="rounded,filled"]
y [fillcolor=gray,style="rounded,filled"]
}](_images/graphviz-668454c0f2d0daa6ea84b72a6a697bf1d8b7fda2.png)
CPoint2D C structure¶
A CPoint2D has just two members,
to store its coordinates:
In [2]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.CPoint2D A
A.x = 1
A.y = 2
printf("A: (%.1f, %.1f)\n", A.x, A.y)
A: (1, 2)
CPoint2D can be allocated and destroyed with these functions:
Note
This functions are rarely used, as C structure in GeomAlgo are usually stack-allocated.
In [3]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.CPoint2D* A
A = ga.new_point2d()
A.x = 1
A.y = 2
printf("A: (%.1f, %.1f)\n", A.x, A.y)
ga.del_point2d(A)
A: (1, 2)
Point2D Python extension type¶
A Point2D takes coordinates as arguments, an optional
index (can be for example vertice indices in a triangulation),
and optional name (used for example by its Point2D.plot method).
-
class
Point2D(x, y, index=0, name=None)¶ Attributes:
-
cpoint2d: CPoint2D*
-
index: int
-
name: string
-
In [4]:
A = ga.Point2D(1, 2, name='A')
B = ga.Point2D(4, 6, name='B')
print('A:', A)
A.plot()
B.plot()
A: Point2D(1.0, 2.0)

The wrapped C structure Point2D.cpoint2d is accessible only using Cython.
In [5]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.Point2D A
ga.CPoint2D* ptr
A = ga.Point2D(1, 2)
ptr = A.cpoint2d
printf("(%.1f, %.1f)\n", ptr.x, ptr.y)
(1, 2)
Get and set coordiantes¶
CPoint2D members are accessed directly to get and set coordinates:
In [6]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.CPoint2D A
A.x, A.y = 1, 2
printf("A: (%.1f, %.1f)\n", A.x, A.y)
A.x, A.y = 4, -5
printf("A: (%.1f, %.1f)\n", A.x, A.y)
A: (1.0, 2.0)
A: (4.0, -5.0)
Point2D as two properties x and y to get/set coordiantes
from/to its underlying cpoint2d attribute:
-
Point2D.x¶
-
Point2D.y¶
In [7]:
A = ga.Point2D(1, 2)
print(A)
A.x, A.y = 4, -5
print(A)
Point2D(1.0, 2.0)
Point2D(4.0, -5.0)
Point operators¶
Points subtraction¶
Two points \(B\) and \(A\) can be subtracted to compute the vector \(\mathbf{AB} = B - A\).
-
void
subtract_points2d(CVector2D* AB, const CPoint2D* B, const CPoint2D* A)¶ Variable
ABmust be already allocated.
In [8]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.CPoint2D A, B
ga.CVector2D AB
A.x, A.y = 1, 2
B.x, B.y = 4, 6
ga.subtract_points2d(&AB, &B, &A)
printf("AB: (%.1f, %.1f)\n", AB.x, AB.y)
AB: (3.0, 4.0)
-
Point2D.__sub__(B, A)¶
In [9]:
A = ga.Point2D(1, 2)
B = ga.Point2D(4, 6)
AB = B - A
print('AB: ({}, {})'.format(AB.x, AB.y))
AB: (3.0, 4.0)
Point plus vector¶
A vector \(\mathbf{AB}\) can be added to a point \(A\) to compute the point \(B = A + \alpha \mathbf{AB}\).
-
void
point2d_plus_vector2d(CPoint2D* B, CPoint2D* A, double alpha, CVector2D* AB)¶ Bmust be already allocated.
In [10]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.CPoint2D A, B
ga.CVector2D AB
A.x, A.y = 1, 2
AB.x, AB.y = 1.5, 2
ga.point2d_plus_vector2d(&B, &A, 2., &AB)
printf("B: (%.1f, %.1f)", B.x, B.y)
B: (4.0, 6.0)
-
Point2D.__add__(A, AB):
In [11]:
A = ga.Point2D(1, 2)
AB = ga.Vector2D(1.5, 2)
B = A + AB*2
print(B)
Point2D(4.0, 6.0)
Points equality¶
Test whether two points \(A\) and \(B\) are strictly equal.
In [12]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.CPoint2D A, B, C
A.x, A.y = 1, 2
B.x, B.y = 1, 2
C.x, C.y = 2, 2
printf("A==B: %d\n", ga.point2d_equal(&A, &B))
printf("A==C: %d\n", ga.point2d_equal(&A, &C))
A==B: 1
A==C: 0
Distance computation¶
Compute the distance between points \(A\) and \(B\).
In [13]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.CPoint2D A, B
double dist
A.x, A.y = 1, 2
B.x, B.y = 4, 6
dist = ga.point2d_distance(&A, &B)
printf("distance: %.1f", dist)
distance: 5.0
-
distance(A, B)¶
In [14]:
A = ga.Point2D(1, 2)
B = ga.Point2D(4, 6)
A.distance(B)
Out[14]:
5.0
Sometime, the knowledge of the square distance is enough, and for performance, computing the square root can be avoided.
In [22]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.CPoint2D A, B
double sdist
A.x, A.y = 1, 2
B.x, B.y = 4, 6
sdist = ga.point2d_square_distance(&A, &B)
printf("square distance: %.1f", sdist)
square distance: 25.0
Various¶
Test if the point \(P\) is left, right, or of an infinite line \((AB)\), through \(A\) to \(B\).
-
is_left(P, A, B, isclose=math.isclose)¶ Returns True if \(P\) is left, False if \(P\) is right, and raises a
ValueErrorif \(P\) is on line AB.compareris a function to test floating point equality.
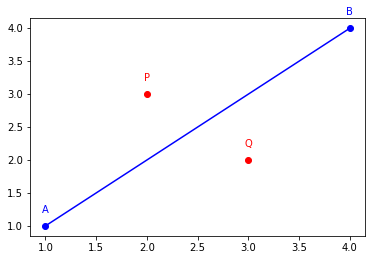
In [2]:
A = ga.Point2D(1, 1, name='A')
B = ga.Point2D(4, 4, name='B')
P = ga.Point2D(2, 3, name='P')
Q = ga.Point2D(3, 2, name='Q')
AB = ga.Segment2D(A, B)
for obj in [A, B, AB]:
obj.plot()
for obj in [P, Q]:
obj.plot(color='red')
print('P is left AB:', P.is_left(A, B))
print('P is left BA:', P.is_left(B, A))
print()
print('Q is left AB:', Q.is_left(A, B))
print('Q is left BA:', Q.is_left(B, A))
P is left AB: True
P is left BA: False
Q is left AB: False
Q is left BA: True
In [3]:
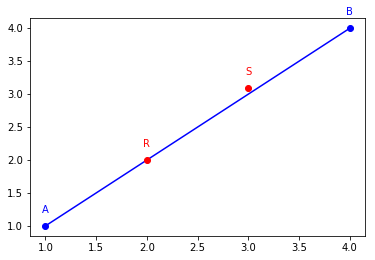
for obj in [A, B, AB]:
obj.plot()
R = ga.Point2D(2, 2, name='R')
S = ga.Point2D(3, 3.1, name='S')
for obj in [R, S]:
obj.plot(color='red')
try:
R.is_left(B, A)
except ValueError as err:
print(err)
print('S is left AB:', S.is_left(A, B))
try:
S.is_left(A, B, isclose=lambda x,y: abs(x-y)<0.5)
except ValueError as err:
print(err)
R in on line (AB)
S is left AB: True
S in on line (AB)
-
double
is_left(CPoint2D* A, CPoint2D* B, CPoint2D* P)¶ - The value returned is:
- Strictly negative if \(P\) is right of the line through \(A\) to \(B\).
- Strictly positive if \(P\) is left of the line through A to B.
- Zero if \(P\) is on the line \((AB)\).
In [27]:
%%cython
from libc.stdio cimport printf
cimport geomalgo as ga
cdef:
ga.CPoint2D A, B, P, R
A.x, A.y = 1, 1
B.x, B.y = 4, 4
P.x, P.y = 2, 3
R.x, R.y = 2, 2
printf('P is left AB: %.2f\n', ga.is_left(&A, &B, &P))
printf('P is left BA: %.2f\n', ga.is_left(&B, &A, &P))
printf('R is left AB: %.2f\n', ga.is_left(&A, &B, &R))
P is left AB: 3.00
P is left BA: -3.00
R is left AB: 0.00
In [ ]: